Decoding Spanish Wine Laws.
Ah, Spain. Land of siestas, fiestas, jamón ibérico, and—of course—vino that spans everything from rustic reds aged in dusty cellars to crisp Albariños served seaside with octopus. If you’ve already explored the strict hierarchies of French AOCs and Italy’s quality-focused DOCGs, prepare to dance to a slightly different beat—because Spain’s wine law is a flamenco of structure, tradition, and a little rebel heart.
Let’s swirl and sip our way through Spain’s classification system and how it compares to its Gallic and Italic cousins—with some myth-busting and lore-taming along the way.
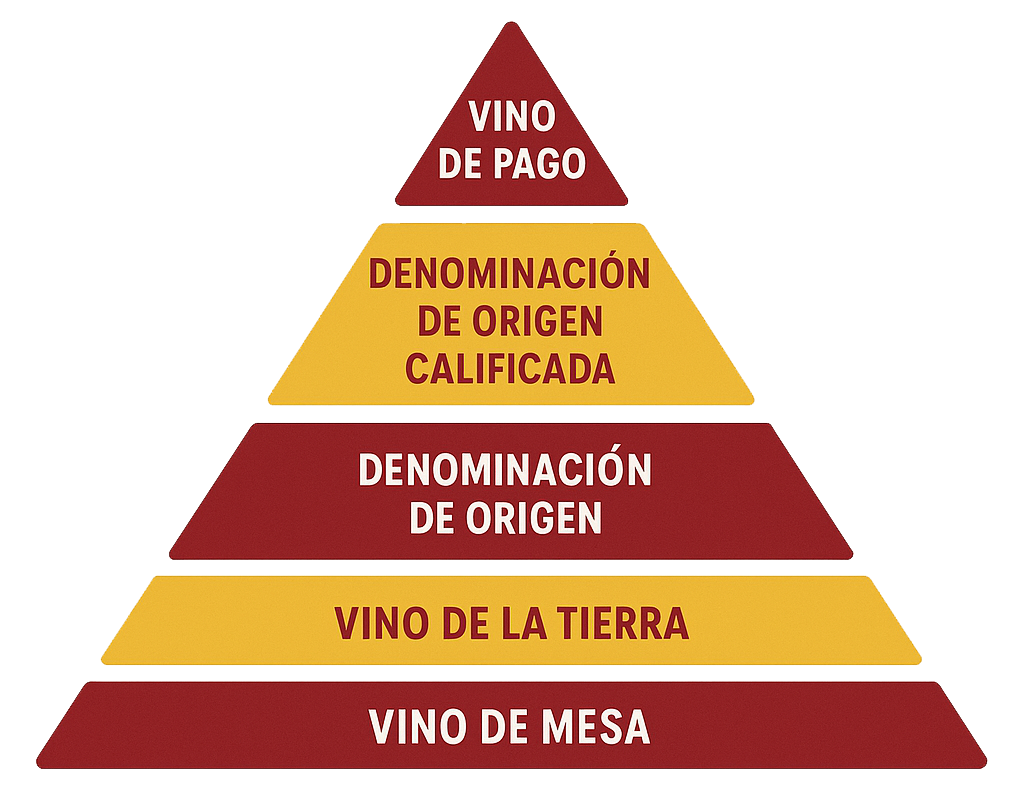
A Pyramid with Flamenco Shoes
Spain’s wine classification system, like France’s and Italy’s, is built on a quality pyramid—but Spain’s version is both more relaxed in practice and more nuanced in regional autonomy.
Here’s the main structure from base to peak:
Vino de Mesa (Table Wine)
The base of the pyramid, now rarely used or exported, these are basic wines with no geographical indication. Often simple blends.
Fun Fact: Due to stricter laws for higher categories, some excellent wines (especially early on) chose to remain labeled as table wine—just like Italy’s famous Super Tuscans did in their rebellious youth.
Vino de la Tierra (VdLT)
Think of this like France’s Vin de Pays or Italy’s IGT. These wines have a geographical indication, but not the stringent rules of higher classifications.
Debunking Time:
“Vino de la Tierra is cheap and low-quality.”
❌ Nope!
While it’s often priced affordably, many boutique producers use VdLT to work outside the box with international varietals or blends. It’s a creative sandbox—like a Tempranillo-Syrah blend from Castilla y León that sings louder than any DO neighbor.
Denominación de Origen (DO)
This is the workhorse of Spanish wine classification—similar to France’s AOC or Italy’s DOC. DO wines must follow specific regulations regarding grape types, yields, aging, and geographic sourcing.
There are currently 70+ DOs, covering famed regions like:
- Rueda – crisp, citrusy Verdejo
- Rías Baixas – home of Albariño
- Priorat – intense reds from old vines
- La Mancha – one of the largest in Europe
- Navarra – a rosado rebel with a growing reputation
Denominación de Origen Calificada (DOCa or DOQ in Catalonia)
Spain’s top-tier designation, reserved for wines from exceptionally consistent regions. So far, only two regions wear this crown:
- Rioja DOCa
- Priorat DOQ (in Catalonia)
How it compares:
- Like Italy’s DOCG and France’s Grand Cru AOC, DOCa wines must pass stricter quality and aging criteria, and the wineries must bottle their wines within the region itself.
Lore-Tamer:
“All the best Spanish wine is from Rioja.”
🚫 Not anymore!
While Rioja deserves its fame, Priorat, Bierzo, Ribera del Duero, and even Canary Island wines are winning hearts, medals, and Michelin-starred wine lists across the globe.
Vino de Pago (VP) – The Spanish Wild Card
Unique to Spain (introduced in 2003), this elite category doesn’t fit neatly into a pyramid. Instead, it elevates individual estates or vineyards that demonstrate top-tier quality and distinctiveness.
To qualify, a pago must:
- Have its own microclimate and terroir
- Use estate-grown grapes only
- Meet DO-level production standards or higher
Examples include:
- Pago de Arínzano
- Pago de Vallegarcía
- Dominio de Valdepusa
Think: Spain’s answer to France’s Grand Cru single-vineyards—but regulated at the national level.

Aging Gracefully
Spain adds another twist: aging classifications that often appear on labels regardless of the region.
Here’s the cheat sheet for red wines (rules vary slightly by region):
| Label | Minimum Aging | Barrel | Bottle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crianza | 2 years | 6 months | 18 months |
| Reserva | 3 years | 12 months | 24 months |
| Gran Reserva | 5 years | 18 months | 42 months |
Note: White and rosado wines require less time overall.
Fun Misconception:
“Gran Reserva = Best wine.”
🤔 Not always. Aging tells you how long it matured, not how good it is. Some wines age beautifully; others lose their soul if forced to sit too long. Context is key—and sometimes a fresh, fruit-forward Crianza pairs better with tapas than a leathery Gran Reserva.
Autonomy and Identity
One major difference between Spain and its neighbors? The autonomous power of regions. Spain’s 17 Autonomous Communities (like Galicia, Catalonia, Andalusia) have significant say in how their DOs are governed. Some even overlap political tensions—Catalonia’s DOs often distinguish themselves from national Spanish identity.
This regional independence is part of what gives Spain such breathtaking diversity—in grapes, styles, and labeling practices.
Native Grapes, No Apologies
Spain is home to over 400 native grape varieties, though fewer than 20 dominate production. Among them:
- Tempranillo – Spain’s signature red grape, known by many names (Tinta del País, Cencibel, Ull de Llebre).
- Garnacha – The Spanish Grenache, spicy and ripe.
- Albariño – Citrus-kissed white from Galicia.
- Verdejo – Zesty, often underestimated.
- Godello, Mencía, Bobal, Trepat – hidden gems waiting to be discovered.
Lore-Tamer:
“Spain = just Rioja reds.”
⛔ Nope. Spain offers volcanic whites from the Canaries, slate-soaked reds from Priorat, coastal charm in Albariño, and fizzy fun in Cava.
Comparative Snapshot: Spain vs France vs Italy
| Feature | Spain | France | Italy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | Vino de Mesa | Vin de France | Vino da Tavola |
| PGI/IGT Tier | Vino de la Tierra | IGP (Vin de Pays) | IGT |
| Main Classification | DO | AOC/AOP | DOC |
| Highest Tier | DOCa/DOQ, Vino de Pago | Grand Cru, Premier Cru (AOC) | DOCG |
| Estate Classification | Vino de Pago | Château system, Grand Cru | Less formalized |
| Aging Terms | Crianza, Reserva, Gran Reserva | Region-dependent | Riserva, Superiore |
| Regional Authority | High autonomy in regions | Centralized via INAO | Mixed (Central and Regional) |
What Makes Spain Special?

Spain’s wine laws balance tradition with experimentation, allowing producers the freedom to create expressive, terroir-driven wines—while offering enough structure to protect authenticity and regional identity.
So whether you’re sipping a flinty Godello from Valdeorras, a powerful Garnacha from Aragón, or a seductive Tempranillo from Ribera del Duero, you’re drinking more than just fermented grape juice.
You’re tasting a nation that knows its roots but isn’t afraid to dance to its own rhythm. 🍷
Cover Photo by Grape Things on Pexels.com





































You must be logged in to post a comment.