Wine, that timeless elixir, has been intertwined with human history for millennia. From ancient amphorae to modern stainless steel tanks, winemaking techniques have evolved, but one tradition remains as steadfast as the vines themselves: aging wine in barrels. This practice is not merely functional but holds a mystical allure, enhancing the flavors, aromas, and textures of wine in ways that transcend mere storage vessels. Let’s dive into the history, craftsmanship, and magic of aging wine in barrels.
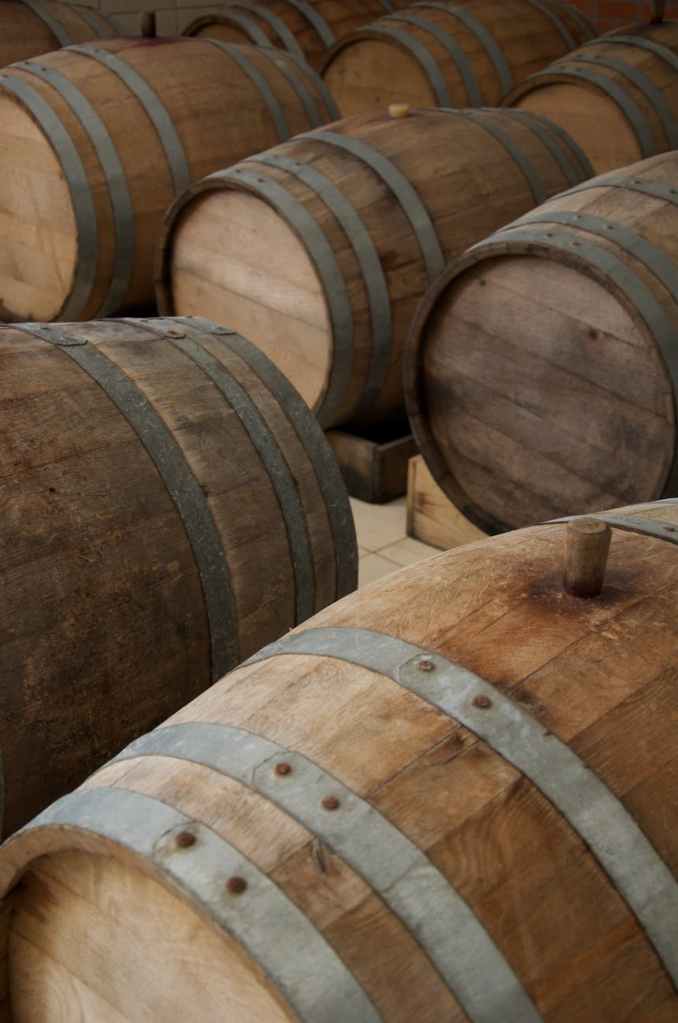

Historical Roots
The art of barrel aging dates back to ancient civilizations, where wooden vessels were used to transport and store liquids. The Romans, in particular, recognized the transformative power of wood on wine, using barrels made from oak to age and transport their precious vintages across their vast empire. Over time, this practice spread throughout Europe, becoming synonymous with the finest wines produced in regions such as Bordeaux, Burgundy, and Rioja.
Barrel aging, the silent maestro of wine evolution, weaves a tapestry of complexity, infusing wines with nuances of oak, whispers of spice, and the symphony of time, crafting bottles of elegance and depth.
Gregory Dean, SOMM&SOMM
Types of Wood
While oak remains the predominant choice for wine barrels, different species and sources of wood impart distinct characteristics to the wine. French oak, known for its subtle flavors of vanilla, spice, and toast, is favored by many winemakers for its elegance and finesse. American oak, on the other hand, tends to impart more pronounced flavors of coconut, dill, and sweet spices, making it a popular choice for bold, fruit-forward wines.
Other types of wood, such as Hungarian oak, Slovenian oak, and chestnut, offer their own unique profiles, adding layers of complexity to the wines they age. Each wood has its own distinct grain, density, and porosity, influencing how it interacts with the wine and shapes its final character.
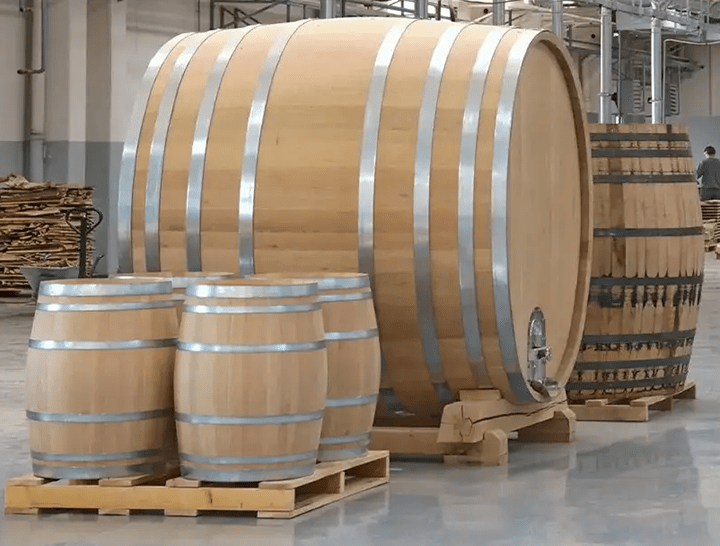

Barrel Sizes and Shapes
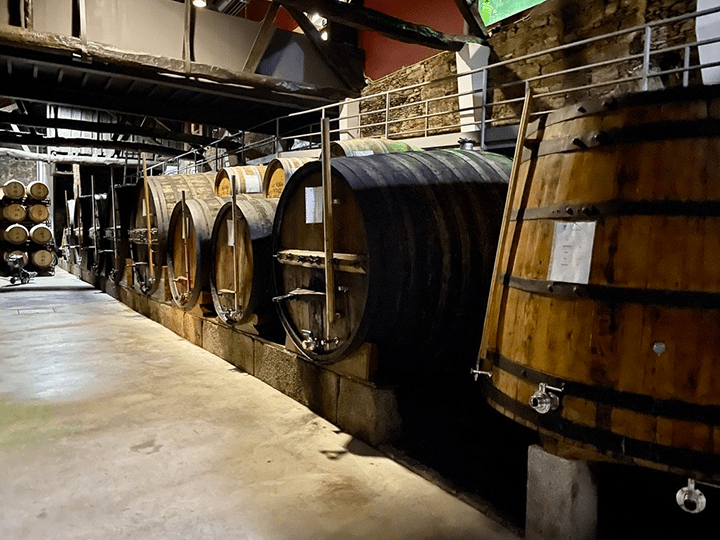
Barrels come in a variety of sizes, from the diminutive barrique to the towering foudre. The standard barrique holds approximately 225 liters (59 gallons) of wine and is commonly used in regions like Bordeaux and Burgundy. Larger formats, such as the puncheon and the foudre, are favored for their reduced surface-to-volume ratio, allowing for slower aging and gentler extraction of flavors.
The shape of the barrel also plays a crucial role in aging wine. Taller, narrower barrels promote more gradual oxidation and evaporation, while shorter, wider barrels encourage faster integration of flavors and textures. Additionally, the toasting level of the barrel—ranging from light to heavy—can be customized to suit the winemaker’s desired style and intensity of oak influence.


Craftsmanship and Cooperage
The art of barrel making, or cooperage, is a centuries-old tradition that requires skill, precision, and patience. Cooperages source the finest oak staves, carefully shaping and toasting them to exact specifications. Master coopers employ time-honored techniques, passed down through generations, to construct barrels that are both functional and beautiful.
Cooperages offer winemakers a range of options, from the type of wood and toast level to the size and shape of the barrel. Customization allows winemakers to tailor their barrels to the specific needs of each wine, ensuring optimal aging and expression of terroir.
Impact on Wine and Cost
The impact of barrel aging on wine is profound, influencing its color, aroma, flavor, and texture in myriad ways. Oak imparts flavors of vanilla, spice, toast, and caramel, while also softening tannins and enhancing mouthfeel. Oxygen slowly permeates the barrel, allowing the wine to evolve and develop complexity over time.
The cost of barrel aging varies depending on factors such as the type of wood, size of the barrel, and quality of craftsmanship. French oak barrels, prized for their elegance and finesse, are among the most expensive, while American oak and other alternatives offer more affordable options. The cost of barrel aging can account for a significant portion of a wine’s production expenses, particularly for premium and ultra-premium wines that require extended aging in oak.

Regional and Varietal Characteristics
Certain countries, regions, and varietals are renowned for the unique characteristics imparted by barrel aging. In Bordeaux, Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot blends mature in oak barrels, gaining complexity and structure over time. Burgundian Pinot Noir and Chardonnay benefit from aging in French oak, acquiring nuances of spice, toast, and vanilla.
Spanish Tempranillo finds its soulmate in American oak, with Rioja and Ribera del Duero wines showcasing flavors of coconut, dill, and sweet spices. Italian Sangiovese, aged in large Slavonian oak casks, develops savory notes of leather, tobacco, and earth.
While barrel aging remains the gold standard for many winemakers, alternative methods offer creative ways to achieve similar results. Stainless steel tanks provide a neutral environment for aging wine, preserving fruit purity and freshness. Concrete eggs and amphorae impart subtle texture and minerality, enhancing the wine’s sense of place.
Some winemakers utilize oak alternatives, such as chips, staves, or spirals, to infuse wine with oak flavors without the expense or commitment of traditional barrel aging. While these methods can produce compelling results, they often lack the complexity and integration achieved through prolonged aging in oak.

Barrels, like fine wine, have a finite lifespan, with each one imparting its unique imprint on the wines it ages. The number of times a barrel can be used depends on factors such as the type of wood, thickness of the staves, and care taken during maintenance. French oak barrels, with their tighter grain and slower oxidation rate, can be reused for several vintages before losing their efficacy.
After a barrel has reached the end of its useful life for aging wine, it may find new purpose as furniture, planters, or even firewood. Some adventurous souls repurpose old barrels as aging vessels for beer, spirits, or vinegar, continuing the cycle of transformation and innovation.
Here’s to the artistry of barrel aging, where time becomes the master craftsman, transforming grapes into liquid poetry. Cheers to the magic of oak, the alchemy of time, and the enduring allure of beautifully aged wines. Salud!
Gregory Dean, SOMM&SOMM
Aging wine in barrels is a time-honored tradition that marries craftsmanship with alchemy, transforming humble grapes into liquid poetry. From the forests of France to the vineyards of Napa Valley, the story of barrel aging is one of passion, innovation, and reverence for the past. As we raise our glasses to toast the fruits of the vine, let us also raise a toast to the humble barrel, the silent guardian of wine’s journey through time and wood. Cheers 🍷







































You must be logged in to post a comment.